Using Quantum Mechanics Describe a Particle in a Box Model
Use ψ-double dot to calculate ψ-dot. Quantum Mechanics Learning Resource Types.
Physics questions and answers.
. The units of the probability density for the particle in 1-D. The Particle in a Box model of quantum mechanics addresses and isolates translational motion. We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts.
If we make the large potential energy at the ends of the molecule infinite then the wavefunctions must be zero at x 0 and x L because the probability of finding a particle with an infinite energy should be. C The zero-point energy of a Heatom in a box is lower than that of an clectron d The position uncertainty is minimum when n1 in the particle in a box. 1 Particle in a Box.
This is most commonly modeled as. The V r 1 potential gives energy level spacing that decreases with energy eventually becoming a continuum for the unbound states. Now I have the following recipe.
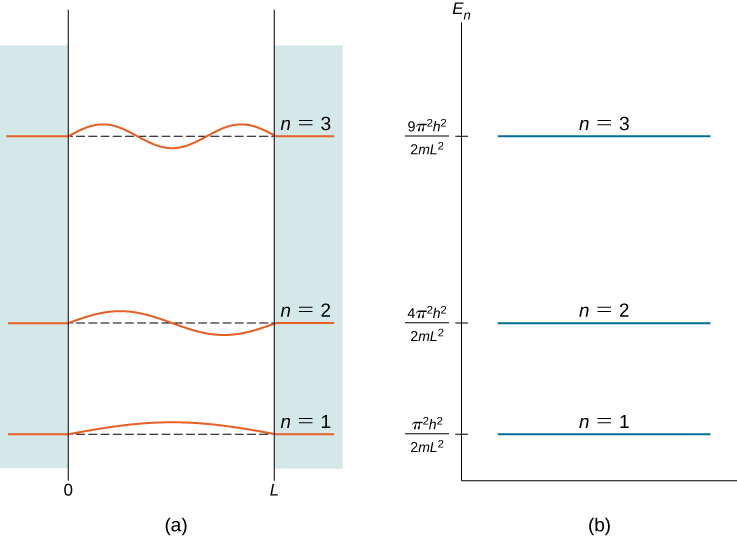
2-D 3-D box are different. N π x L En U 0 n2h2 8mL2 E n U 0 n 2 h 2 8 m L 2. Draw the wave function and probability distribution of the particle upto n 4.
As a concrete illustration of these ideas we study the particle in a box in one dimension. Using the quantum particle in a box model describe how the possible energies of the. Textbook solution for University Physics Volume 3 17th Edition William Moebs Chapter 7 Problem 14CQ.
The particle in a one-dimensioanl infinite potential well also known as the one-dimensional particle in a box. It shows the essence of quantization - presence of discrete energy levels. So what it shows is that in any real setup a particle in a box is bound to explore in various ways a set of fixed patterns which are the standing waves we learn in school and that is the reason why they are importantin two dimensions.
A particle in a 3-dimensional box is a fundamental quantum mechanical approximation describing the translational motion of a single particle confined inside an infinitely deep well from which it. Explain what is wrong with the following reasoning. Particle in a box PDF - 12MB Particle in a box PPT - 69MB 41 Reflection from a potential step PDF - 20MB.
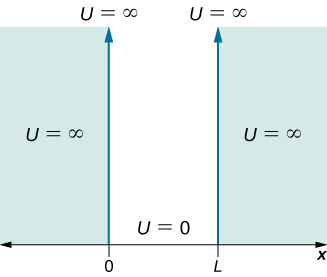
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. This model also deals with nanoscale physical phenomena such as a nanoparticle trapped in a low electric potential bounded by high-potential barriers. This is just a particle of mass which is free to move inside the walls of a box but which cannot penetrate the walls.
We represent that by a potential which is zero inside the box and infinite outside. The particle in an infinite potential well 1-D box is the simplest quantum mechanical bound state problem to solve. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems.
In classical systems for example a particle trapped inside a large box can move at any speed within the box and it is no. The particle in a box potential. N 123 n 1 2 3.
2 2-dimensional particle-in-a-box problems in quantum mechanics from which the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions can simply be read off. ψnx 2 L sin nπx L ψ n x 2 L sin. Short lecture demonstrating particle in a box wavefunctionsThe particle in a box is a quantum mechanical model system for a particle which is restricted to.
Spectral analysis can be accomplished by straightforward appeal to methods borrowed from algebraic number theory while study of interrelationships among the. The quantum particle in a box model has practical applications in a relatively newly emerged field of optoelectronics which deals with devices that convert electrical signals into optical signals. Use Schrödingers equation to calculate ψ-double dot.
Classical physics the collection of theories that existed before. Particle in a 3-Dimensional box - Chemistry LibreTexts. In quantum mechanics the particle in a box model describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers.
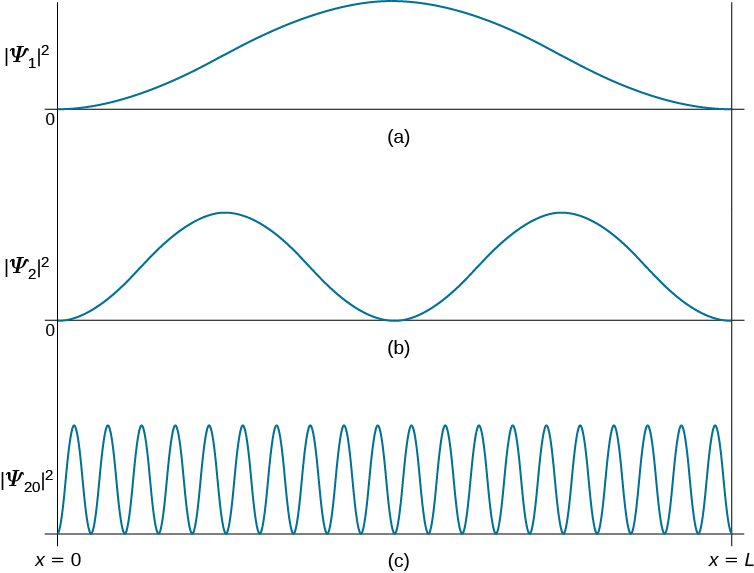
We solve the Schrödinger equation inside the box and realize that the probability for. We can go a little bit further in our quest for understanding the quantum behaviour of a particle in a box. For a quantum particle in a box the first excited state Ψ 2 Ψ 2 has zero value at the midpoint position in the box so that the probability density of finding a particle at this point is exactly zero.
So what quantum mechanics tells you is an energy measurement of a particle in a box cannot give a random. Start at x 0 m and ψ 0 also I will pick ψ-dot equal to zero. Using the quantum particle in a box model describe how the possible energies of the particle are related to the size of the box.
These are a class of quantum mechanical problems whereby we see by simple mathematics that the energy levels of certain quantum systems are discretely quantized. In general in quantum mechanics we cannot make these probabilities go exactly to zero but we can consider the idealization that the forces are sufficiently strong to make the probabilities as close to zero as we like. Accessibility Creative Commons License Terms and Conditions.
11 It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry quantum field theory quantum technology and quantum information science. The harmonic potential V r 2 gives evenly spaced energy levels. This post explores the simplest quatnum mechanical system.
If the probability of finding a quantum particle at the midpoint is zero the particle is never at this point right. The box is completed by applying a similar repulsive force at so that the probability of finding the particle at locations is also extremely small. The particle in a box is the very first example most people see of a bound state problem.
B The particles in a 1-D 2-D 3-D box can all have degenerate energy levels. A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 and the square of every one of them will give you the odds that you will find this energy or that energy or some other energy. It is straightforward to extend it to higher dimensions.
For the particle-in-a-box the particle is restricted to the region of space occupied by the conjugated portion of the molecule between x 0 and x L.
The Quantum Particle In A Box University Physics Volume 3
Quantum Chemistry 3 5 Particle In A Box Youtube

No comments for "Using Quantum Mechanics Describe a Particle in a Box Model"
Post a Comment